Playing is Learning
The Workings of the Human Feet
June 17th, 2015
| Ads | ||
|
Play the Challenge
|
||
|
A New Word is Coined A new Character is revealed A new Game is Afoot |
An Edutainment Adventure Based on Three Rounds of Investigations
|
|
|
Welcome to the World of PROFESsee™by seeCOSM™ PROFESsee™ is my title. I am the perpetual learner, in pursuit of knowledge, wisdom and truth. I derived my name from professor |
 |
|
|
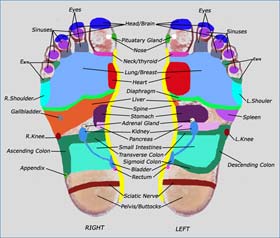
The human foot is made up of many muscles, bones and joints. All these work together to achieve the main functions and movements that the feet are known for. These movements or activities cannot be achieved without the help of the bones, joints and muscles. In short, all of them work together in unison to ensure that the function of the feet become a reality. In its places, the foot performs more functions and activities than other parts of the body. This includes upward direction of the inner and outer foot, inversion and evasion, turning of the toes inwards and outwards, adduction, dorsiflexion, pointing the foot upwards and downwards, abduction and planter flexion. The human feet achieve all these movements through the workings of the two types of feet muscles. These are the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. The intrinsic muscles on their own are divided into three. These include the extrinsic anterior, lateral and posterior muscles. Extrinsic anterior muscles consist of the muscles that are located in the front of the leg, and which run through the top of the human foot. They include the extensor hallucis longus, tibialis anterior, peroneus tertius and extensor digitorum longus. The main function of these is to help the feet to step forward when walking. They also help in dorsiflexion. The peroneus tertius as well helps the toe with evasion. The extrinsic lateral muscles run through the outer part of the leg, and they include the peroneus brevis and the peroneus longus. Their function is to lend support to the arches. They also stabilize the ankle and maintain balance. The extrinsic posterior muscles are the muscles that run through the back of the human leg and connect at the bottom of the foot. They include the flexor hallucis longus, gastrocnemius and soleus, flexor digitorum longus and tibialis posterior. They help the feet with planter flexion, arch support and inversion. The intrincic muscles include extensor digitorum brevis and extensor digitorum longus, and these help the foot with dorsiflexion. The interossei which consists of seven different muscles helps the foot to walk and spread the toes. The flexor hallucis brevis helps the big toe to planter flexion; adductor hallucis helps it with abduction, while the flexor digiti minimi brevis helps the small toes to planter flexion. Can you Zoom to the foot's component and answer the question? Image courtesy of: http://www.healthy-aging-for-women-babyboomers.com/human-foot.html |
||
Latest News / Events
E-mail [email protected]
The Professee™ Newsletter Beta
http://www.seecosm.com/
http://www.seecosm.com/

